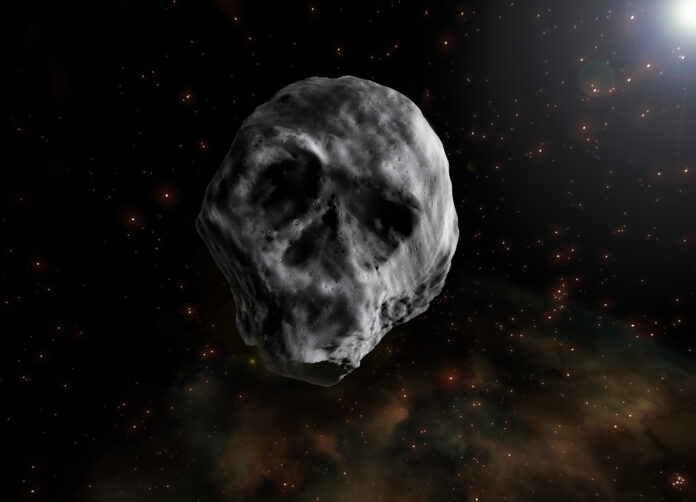
A haunting human skull-shaped Halloween Asteroid is fast approaching planet Earth as it rushes through our solar system at a tremendous speed. According to cosmologists, the asteroid “2015 TB145” will be hurtling towards our planet in 2018 and such an encounter won’t be seen until 2088.
The same asteroid passed by Earth on Oct. 31, 2015 (Halloween), but did not create any impediments. However, this time it seems to be on an overdrive mode. Cosmologists are studying about this weird asteroid to decipher if it could cause any impacts or not.
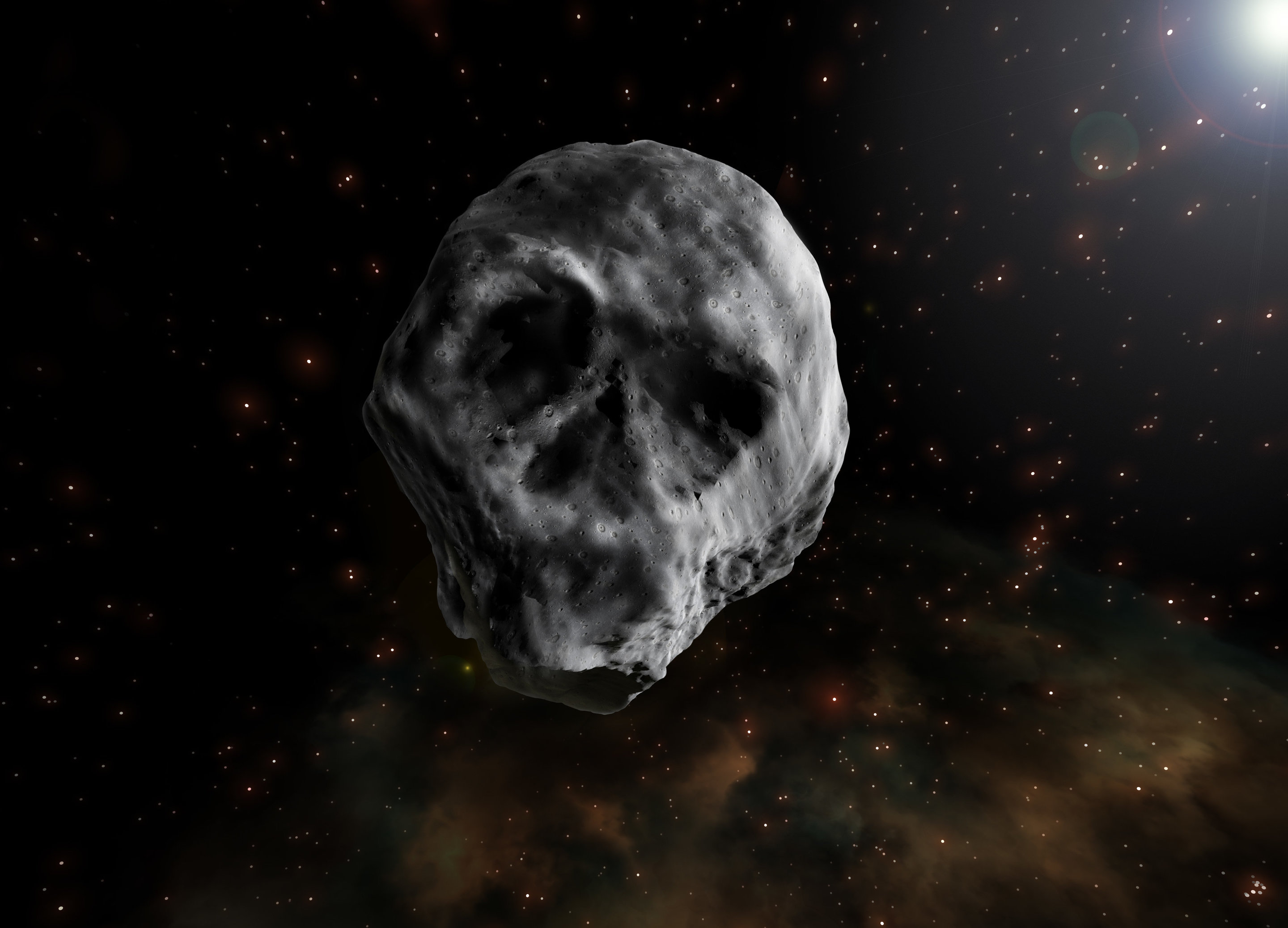
A group of scientists in October 2015 used the Pan-STARRS telescope in Hawaii to first spot this mysterious asteroid that eerily resembles a human skull vis-à-vis shape and features such as the ‘eyes’ and ‘nose.’ They also determined that the asteroid completes one rotation every 2.94 hours and only reflects about 5-6 percent of sunlight that beams on it.
According to Pablo Santo-Sanz, an astrophysicist at the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia in Spain, “the 2015 TB145 asteroid is very dark, and only slightly more reflective than charcoal.”
It was spotted flying across Earth about 486,000 km away or approximately 1.3 times the distance to the moon. So, how big is it? This ghoulishly weird Halloween Asteroid is approximately 2,100 foot or 640 meters wide, and is expected to fly past the Earth in mid-November 2018.
Astronomers in NASA, as well as from around the world, have been relentlessly working to figure out the characteristics of the asteroid 2015 TB145 and hope to get more data as it rushes through our solar system again in 2018.

However, herein lies the caveat. This time around the asteroid will pass at a further distance from Earth than it did the back in 2015. Astronomers believe that the Halloween Asteroid could quite possibly be a lost/extinct comet that got rid of its volatile compounds and water after continuously orbiting the sun many times.
Although comets have a significant composition of ice and rock, asteroids are primarily made up of a metallic rocky substance which makes it hard to identify them with surety. Moreover, their orbits are also of different types.

